Add: Tongji Industrial Zone,JimoQingdao China 266228
Mobile: 86-18653233625 (WhatApp, WeChat)
E-mail: info@segerindustrial.com
Tel: 86 532 68893719
Fax:86 532 85698271
April 20, 2021
1. Macro Inspection
The supplied processing steel hasn’t made re-inspection in the factory.After
forging,many reticular cracks are appeared on the surface of big and small head(It’s the surface defect according to the defect locations),almost falling off severely(see Fig.4 and Fig.5) .After inspecting the forging temperature, there’s no over-burning phenomenon.
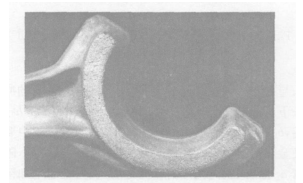
Fig. 4 Surface chap on la rge head
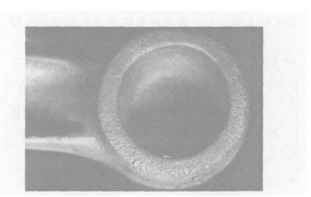
Fig . 5 Surface chap o n little head
2. Crack Analysis
Observe the un-corroded sample(Remove 2mm parallel to the surface for sample preparation ),it is found that there is oxidation at the grain boundary, and there are gray oxide inclusions in the cavity of the crack, extending inward along the grain boundary; After the sample was eroded by 4%HNO3, decarburization layer can be seen on both sides of the crack, and its depth is 0. 15 ~ 0. 2mm,and part of yellow free copper can be observed along the grain boundary near the crack(see Fig.6).The chemical composition of the connecting rod was further analyzed, and the copper content (mass fraction) was 0.374%. According to literature [3, 4], when the copper content is> 0.2%, cracking will occur during forging. So the high copper content is the main reason for surface cracking of this batch of connecting rods. It is easy to produce surface cracking during forging. Why surface cracks are only generated on the head of the connecting rod, but not on the rod This is caused by the difficulty of forming.Compare the small end of the connecting rod with the rod. From Fig. 7, they are all formed by pressing down the punch in the center to squeeze the metal into the cavity, because h1 /d1> h2 / d2, b1> b2 , And a1 <a2, which means that it is more difficult for the head to fill the cavity with metal during the forging process than for the rod. In the later stage of deformation, with the continuous decrease of a1 value, the deformation resistance increases, and it can only be completed by increasing the number of hammer strokes.During the forging process, the deformation of the top metal is turned from inside to outside to fill the cavity, and due to the copper phase, the strong surface tension causes the B plane of the connecting rod head to tear and crack.
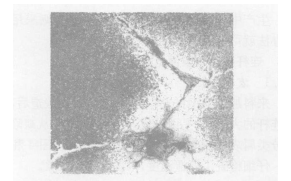
Fig . 6 Cry stal bound oxidation and copper compound
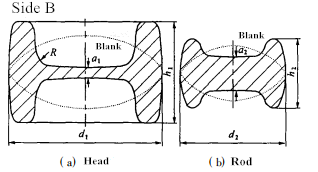
Fig.7 Shape comparision of head and rod
3. Solution
(1)Stop using this material to avoid cracks.
(2) Appropriately increase the draft angle, a and R value of the connecting rod head to make the metal flow more smoothly during the forging process